Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized numerous industries, enabling machines to perform complex tasks and make informed decisions. Within the realm of AI, two prominent techniques have emerged: generative AI and predictive AI. While both approaches utilize machine learning algorithms, they differ in their core objectives and applications. In this blog, we will explore the distinctions between generative AI and predictive AI, shedding light on their unique capabilities and real-world applications.
Generative AI: Creating Something New
Generative AI focuses on the creation of new content, generating outputs that are original and novel. It leverages techniques such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and Autoregressive Models to learn patterns and distributions from existing data and generate new samples. Generative AI models have the ability to generate realistic images, compose music, write text, and even design virtual worlds.
The key characteristic of generative AI is its ability to create something that does not exist in the training data explicitly. It captures the underlying complexity and diversity of the input and produces unique outputs that exhibit creativity and originality. This makes generative AI a powerful tool for artists, designers, and content creators seeking to explore new frontiers and push the boundaries of human creativity.
Predictive AI: Forecasting Future Outcomes
Predictive AI, on the other hand, focuses on analyzing patterns in existing data to make accurate predictions and forecasts about future outcomes. It utilizes machine learning algorithms such as regression, classification, and time series analysis to learn from historical data and identify patterns and relationships. Predictive AI models can be trained to predict stock market trends, customer behavior, disease progression, and much more.
The primary objective of predictive AI is to extract valuable insights and make informed predictions based on available data. It aids decision-making processes, allowing businesses to optimize operations, identify potential risks, and develop data-driven strategies. Predictive AI is widely used in finance, marketing, healthcare, and numerous other industries where accurate predictions can drive competitive advantage and operational efficiency.
Generative AI Applications and Use Cases
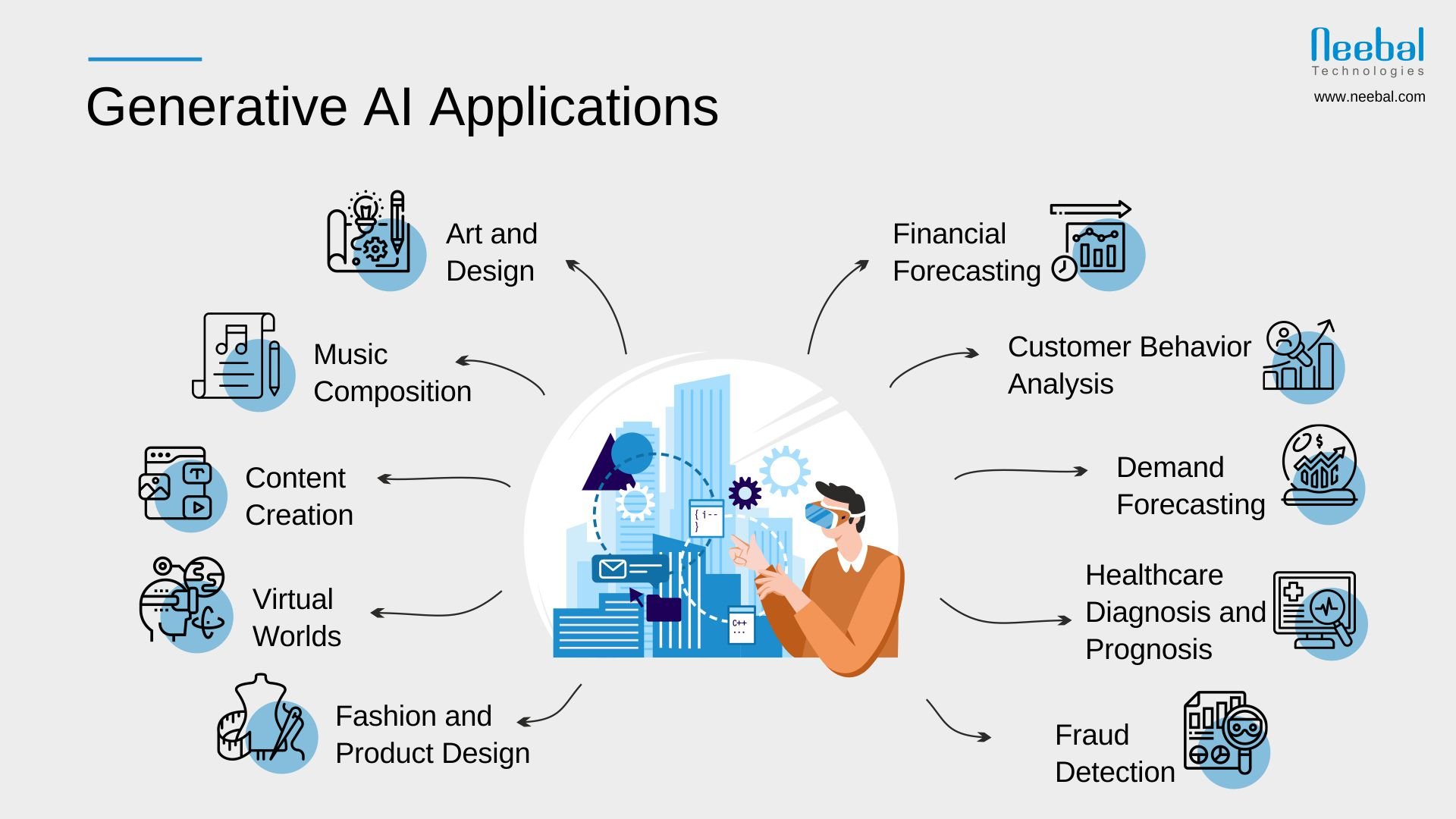
Generative AI and predictive AI find applications in distinct domains, each offering unique advantages and capabilities:
- Art and Design: Generative AI enables artists and designers to create unique artwork, generate new design concepts, and explore novel styles and compositions.
- Music Composition: Generative AI tools can compose original music tracks, remix existing compositions, and experiment with new genres and styles.
- Content Creation: Generative AI facilitates the generation of text, images, and videos, streamlining content creation processes and enabling personalized experiences.
- Virtual Worlds: Generative AI models are used to design and populate virtual environments in video games, simulations, and virtual reality experiences.
- Fashion and Product Design: Generative AI assists in creating new fashion designs, optimizing product aesthetics, and predicting fashion trends.
Predictive AI Applications
- Financial Forecasting: Predictive AI models analyze historical financial data to predict stock market trends, forecast investment opportunities, and assess financial risks.
- Customer Behavior Analysis: Predictive AI enables businesses to analyze customer data, predict purchasing patterns, and personalize marketing strategies.
- Demand Forecasting: Predictive AI models can anticipate future demand for products or services, optimizing inventory management and supply chain operations.
- Healthcare Diagnosis and Prognosis: Predictive AI aids in disease diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment planning, assisting healthcare professionals in making informed decisions.
- Fraud Detection: Predictive AI helps identify fraudulent activities, enabling businesses to prevent financial losses and protect against cyber threats.
Conclusion
Generative AI and predictive AI represent two distinct approaches within the broader field of artificial intelligence. Generative AI focuses on creating original and novel content, while predictive AI aims to forecast future outcomes based on historical data patterns. Each approach has its unique applications and use cases, empowering different industries and domains.
By understanding the distinctions between generative AI and predictive AI, organizations and individuals can leverage the strengths of each approach to drive innovation, enhance creativity, and make informed decisions. As AI continues to evolve, the synergistic combination of generative and predictive techniques holds the potential to unlock new opportunities and shape the future of intelligent systems.
