The next stage of digital transformation is Hyperautomation, a concept that emerged from the convergence of machine learning, artificial intelligence, and robotic process automation. The Gartner IT Glossary defines it as an approach where organizations automate as many business processes as possible using tools like AI and machine learning. With the growing data pools that Hyperautomation utilizes, data security has become a central concern.
While Hyperautomation has the potential to revolutionize business operations, it also presents unique challenges for data security. In fact, a report by Identity Theft Resource Center (ITRC) states that the number of cyberattacks against organizations has gone up by 68%. Hence, the necessity of framing Hyperautomation within the context of trust and compliance has emerged as a critical business requirement.
Understanding Hyperautomation
At its core, Hyperautomation refers to the use of advanced technologies, including AI and machine learning, to automate tasks previously requiring human intervention. It also involves the orchestration of work and the ability to understand, learn, analyze, adapt, and even predict outcomes.
Global NewsWire reports that the global Hyperautomation market is expected to reach US$ 155 Billion by 2032. These figures underscore the growing reliance on Hyperautomation across industries. From banking and retail to healthcare and logistics, Hyperautomation is redefining operational efficiencies, decision-making, and customer experiences.
Hyperautomation and Data security
However, with great power comes great responsibility, and Hyperautomation is no exception. The increasing volume, velocity, and variety of data processed through Hyperautomation systems augment the complexities of ensuring data security. The intricate interplay of multiple technologies in a hyperautomated environment makes it susceptible to diverse security threats.
According to Forbes, the annual cost of cybercrime globally is projected to reach $10.5 trillion by 2025, partially due to vulnerabilities in hyperautomated systems. Hence, it is essential to have robust security controls, risk assessment mechanisms, and incident response plans to ensure data security in hyperautomated environments.
The Trust Factor in Hyperautomation
Trust is a critical cornerstone of Hyperautomation. Stakeholders, including customers, employees, and partners, must trust that their data is secure within hyperautomated systems. A breach of this trust can lead to severe reputational damage and significant financial losses.
A PwC survey revealed that 85% of consumers will not do business with a company if they have concerns about its security practices. Therefore, maintaining robust data security is not just a compliance requirement but also a business imperative for building and sustaining trust.
Compliance Perspectives on Hyperautomation and Data Security
As the integration of Hyperautomation within organizational structures proliferates, it's crucial to navigate the expansive and constantly evolving regulatory terrain tied to data security. Key international legislation, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) of the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, stipulates rigorous data security protocols. Notably, these regulations are applicable to data processed through hyperautomated systems, underscoring the need for these systems to be designed and operated in adherence to data security laws.
Non-compliance with these stringent regulations can lead to punitive measures, often in the form of substantial financial penalties. For instance, in the year 2022 alone, fines imposed under GDPR exceeded a staggering €2,34 bn. The figures underline the importance of being conversant with and adhering to all pertinent regulatory obligations relating to Hyperautomation and data security. Avoidance of steep fines is just one aspect; the larger objective is to foster a culture of compliance that underscores the organization's commitment to secure data handling.
Practical Steps Towards Ensuring Data Security in Hyperautomation
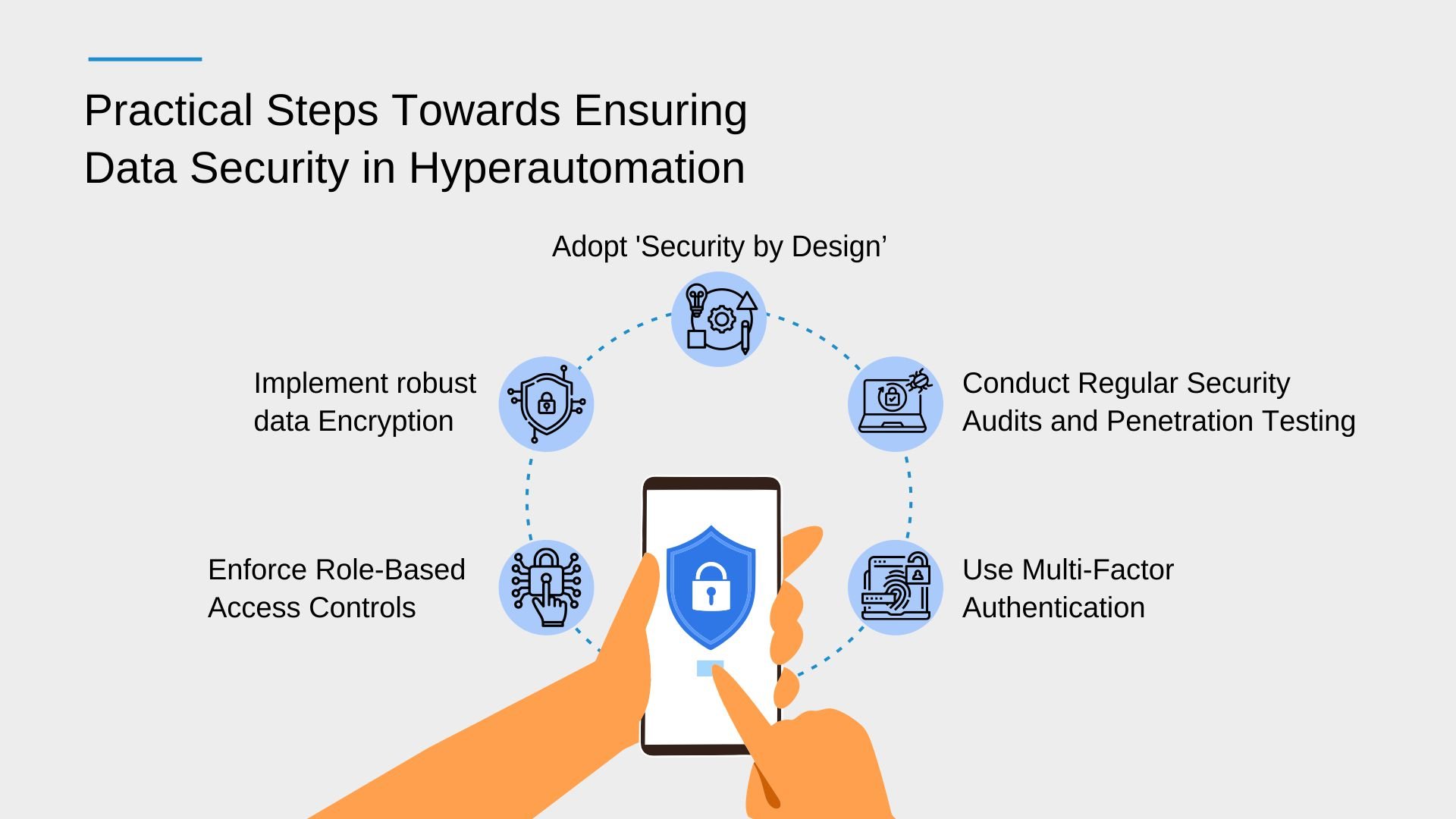
The journey to secure hyperautomated systems is paved with multiple strategic measures. Below are some practical steps toward ensuring data security in Hyperautomation.
Adopt 'Security by Design': Organizations should consider adopting the 'Security by Design' approach, as recommended by Gartner. This approach implies integrating security considerations right from the conceptualization and design phases of Hyperautomation processes, rather than adding them as an afterthought.
Implement robust data Encryption: Encrypting data, both when it is at rest and in transit, is crucial to preventing unauthorized access. Advanced encryption algorithms and techniques should be used to safeguard the integrity and confidentiality of data.
Enforce Role-Based Access Controls: Implementing role-based access controls can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive data. By providing access rights based on the roles and responsibilities of individuals, organizations can ensure that only authorized personnel have access to critical information.
Conduct Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Regular security audits and penetration testing are essential to identify potential vulnerabilities and rectify them promptly. These procedures aid in assessing the efficacy of the security measures in place and expose any flaws that potentially allow for malicious entities to exploit them.
Use Multi-Factor Authentication: Multi-factor authentication requires users to provide multiple pieces of evidence to confirm their identities. Implementing this can provide an additional layer of security, making it more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access to critical systems and data.
Conclusion
Trust, being a critical element, hinges on how securely data is managed in a hyperautomated environment. Similarly, compliance with data security regulations is not just about avoiding penalties; it's about demonstrating a commitment to protecting stakeholder interests.
As Hyperautomation continues to be at the forefront of digital transformation, businesses must prioritize data security. By taking proactive steps, companies can leverage the power of Hyperautomation while ensuring data security, thereby enhancing trust and compliance. It’s not just about being technologically advanced; it’s about being technologically responsible.
