Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) are the backbone of many economies worldwide, contributing significantly to economic growth and job creation. However, SMEs often face resource and operational challenges, making it essential for them to find new solutions to stay competitive in a rapidly changing business landscape.
In this blog post, we will explore the concept of hyperautomation and how it can empower SMEs to thrive in the digital age.
What Is Hyperautomation?
Hyperautomation is a strategic approach that combines various technologies, including Robotic Process Automation (RPA), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, data analytics, and other advanced tools, to automate and optimize business processes comprehensively.
It aims to improve decision-making, augment human capabilities, and improve overall business operations. In the context of SMEs, hyperautomation becomes a game-changer by enabling them to compete with larger enterprises without incurring significant operational costs.
Benefits of Hyperautomation for SMEs
- Productivity - Hyperautomation simplifies routine, time-consuming tasks and frees up employees to focus on more value-added activities. This increase in efficiency can lead to substantial time and cost savings.
- Precision - Automated processes are less prone to errors compared to manual tasks. SMEs can maintain data accuracy, reducing the risk of costly mistakes and enhancing the quality of their products or services.
- Cost Effective - By automating tasks that would typically require human resources, SMEs can significantly reduce operational costs. This includes the costs associated with hiring and training employees for repetitive tasks.
- Reliability - One of the significant advantages of hyperautomation is its ease of use. As SMEs grow, they can easily adapt and add more automated processes to accommodate increased demand without the need for extensive manual work.
- Insights - Hyperautomation tools provide valuable data and insights. SMEs can use these insights to make informed decisions, better understand customer behavior, and improve their business strategies.
- Customer Experience - With the ability to automate customer service, data analysis, and other processes, SMEs can provide a more efficient and personalized experience to their users.
Key Components of Hyperautomation
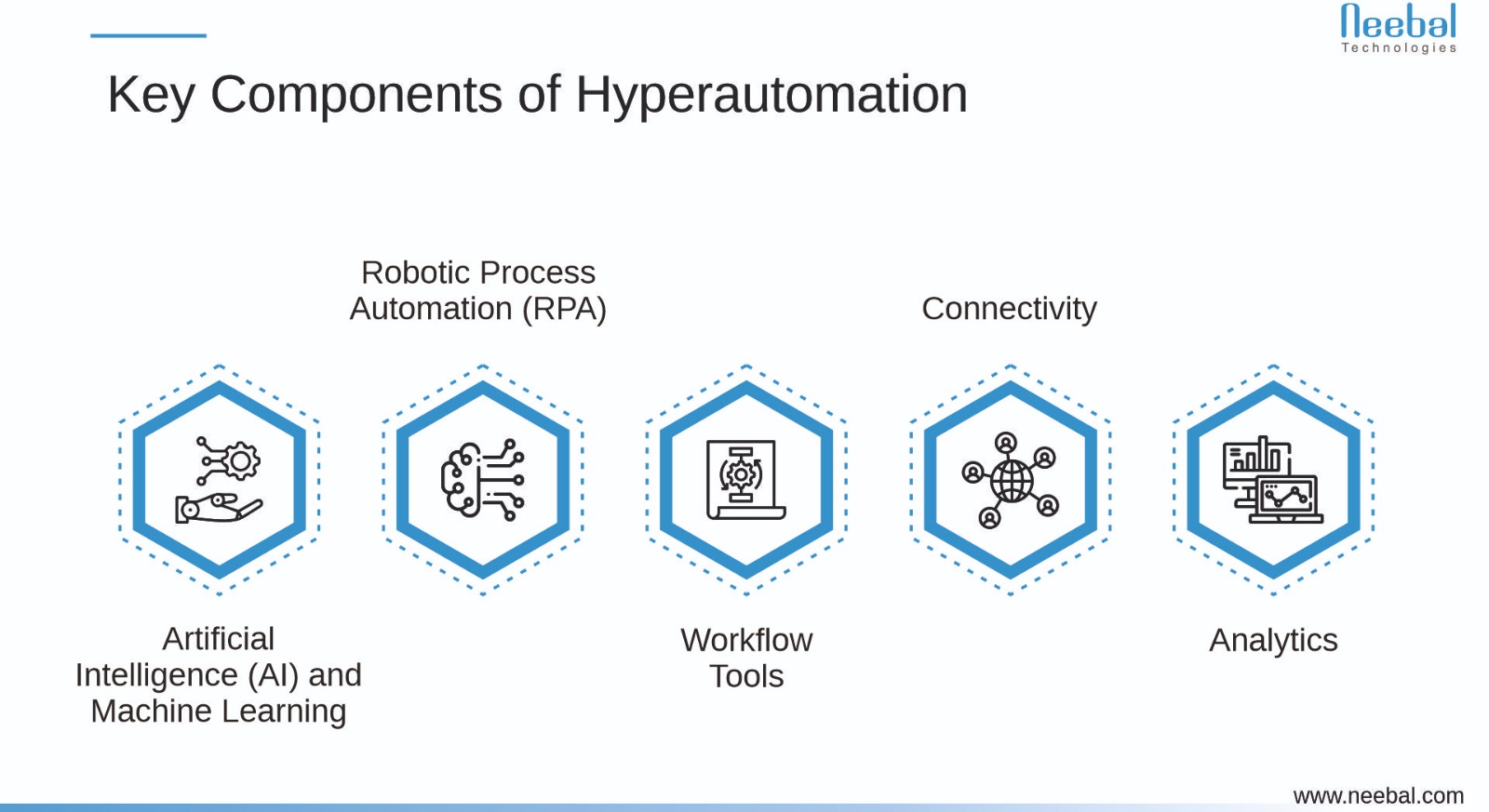
To implement hyperautomation effectively, SMEs need to understand its key components:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning - AI and machine learning enable SMEs to analyze data, predict trends, and make more informed decisions. Chatbots, for instance, can automate customer support and provide immediate responses to inquiries.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) - RPA involves using software robots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks, such as data entry, invoice processing, and report generation. SMEs can make use of RPA to streamline internal operations, reduce errors, and improve process efficiency.
- Workflow Tools - Workflow automation tools allow SMEs to define, execute, and monitor various business processes. This can include automating document approvals, onboarding procedures, and order processing.
- Connectivity - SMEs can use integration platforms to connect various software applications and databases, ensuring a seamless flow of information and data exchange.
- Analytics - Hyperautomation relies on data analytics to generate insights, measure performance, and identify areas for improvement. SMEs can use analytics tools to track customer behavior, financial data, and more.
What is the Need for Hyperautomation Tools?
Unlike traditional automation that was just mimicking human actions, the rise of AI-driven hyperautomation tools has led to a standard shift in how businesses operate.
The advantages of hyperautomation are numerous: it is purpose-built and applied to certain business processes, and it is revolutionizing in this way. Businesses may now quickly automate complex operations, allowing staff to focus on higher-value activities that are more important.
Use Cases for Hyperautomation in SMEs
- Finance and Accounting - Hyperautomation can simplify financial processes, from invoice processing and payroll to budget forecasting and financial reporting. This not only reduces human errors but also helps SMEs make better financial decisions.
- Inventory Management - Efficient inventory management is vital for SMEs. Hyperautomation can automate inventory tracking, reordering processes, and demand forecasting, helping SMEs increase stock levels and decrease carrying costs.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) - SMEs can automate CRM processes to manage leads, nurture customer relationships, and provide personalized communication. This results in improved customer experiences and growth in customer loyalty.
- Hiring Process - Automation can be employed in the hiring process, including candidate screening, interview scheduling, and onboarding procedures. This not only saves time but also ensures a consistent and organized hiring process.
- E-commerce and Sales - For SMEs in the e-commerce sector, hyperautomation can streamline order processing, inventory management, and customer communications. This results in faster order fulfillment and improved customer satisfaction.
Challenges and Considerations
While hyperautomation offers numerous benefits, SMEs should be aware of the challenges and considerations:- Investment - Implementing hyperautomation requires an initial investment in technology and training. SMEs need to carefully assess their budget and potential return on investment (ROI).
- Change in Mindset - Employees may resist automation due to fears of job displacement. SMEs need to focus on changing management strategies to ensure that their workforce embraces automation as a means to leverage their roles.
- Data Security - With the automation of sensitive data, SMEs must prioritize data security and compliance with data protection regulations.
- Scalability - As SMEs grow, their hyperautomation systems need to scale accordingly. Ensuring that the chosen technologies can grow with the business is crucial.
The Future of Hyperautomation and SMEs
The future of SMEs and hyperautomation holds the promise of greater efficiency, cost reduction, and scalability. However, it also comes with the responsibility of ethical and secure data handling, as well as fostering a workforce that is adaptable and comfortable working alongside automation. As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of hyperautomation will expand, offering even more opportunities for SMEs to optimize their operations.
Conclusion
In a competitive world where efficiency is most important, hyperautomation presents SMEs with a powerful solution to thrive and grow. By embracing the holistic approach of hyperautomation, SMEs can simplify processes, reduce operational costs, and provide better services to their customers. While challenges exist, the benefits outweigh them, making hyperautomation a strategic investment.
